he conditions of rotation indicate the motion of one bearing ring with respect to the load direction and are expressed as either circumferential load or point load
Point load
If the ring remains stationary relative to the load direction, there are no forces that displace the ring relative to its seating surface. This type of load is described as point load.
There is no risk that the seating surface will be damaged and a loose fit is possible.
Circumferential load
If forces are present that displace the ring relative to its seating surface, every point on the raceway is subjected to load over the course of one revolution of the bearing. A load with this characteristic is described as a circumferential load.
Conditions of rotation
| Conditions of motion | Example | Schematic | Load case | Fit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Rotating inner ring Stationary outer ring Constant load direction |
Shaft with weight load |
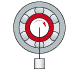 |
Circum- ferential load on inner ring |
Inner ring: tight fit necessary Outer ring: loose fit permissible |
|
Stationary inner ring Rotating outer ring Load direction rotates with outer ring |
Hub bearing arrangement with significant imbalance |
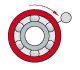 |
and Point load on outer ring |
|
|
Stationary inner ring Rotating outer ring Constant load direction |
Passenger car front wheel bearing (hub bearing arrangement) |
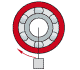 |
Point load on inner ring |
Inner ring: loose fit permissible Outer ring: tight fit necessary |
|
Rotating inner ring Stationary outer ring Load direction rotates with inner ring |
Centrifuge, vibrating screen |
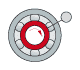 |
and Circum- ferential load on outer ring |

