NTN rolling bearings are available in a variety of types, configurations, and sizes. When selecting the correct bearing for your application, it is important to consider several factors, and analyse in various means.
As a general guideline, the basic procedure for selecting the most appropriate bearing is shown in the following flow chart. you can also refer to SKF bearing selection.
NTN bearing selection flow chart
| Procedure | Confirmation items |
|---|---|
| Confirm operating conditions and operating environment |
|
| Select bearing type and configuration |
|
| Select bearing dimensions |
|
| Select bearing tolerances |
|
| Select bearing’s internal clearance |
|
| Select cage type and material |
|
| Select lubricant, lubrication method, sealing method |
|
| Select any special bearing specifications |
|
| Confirm handling procedures |
|
Selection of NTN bearing type and configuration
Dimensional limitations
The allowable space for bearings is generally limited. In most cases, shaft diameter (or the bearing bore diameter) has been determined according to the machine’s other design specifications. Therefore, bearing’s type and dimensions are determined according to bearing bore diameters. For this reason all dimension tables are organized according to standard bore diameters. There is a wide range of standardized bearing types and dimensions: the right one for a particular application can usually be found in these tables.
Bearing load
The characteristics, magnitude, and direction of loads acting upon a bearing are extremely variable. In general, the basic load ratings shown in bearing dimension tables indicate their load capacity. However, in determining the appropriate bearing type, consideration must also be given to whether the acting load is a radial load only or combined radial and axial load, etc. When ball and roller bearings within the same dimension series are considered, the roller bearings have a larger load capacity and are also capable of withstanding greater vibration and shock loads.
Rotational speed
The allowable speed of a bearing will differ depending upon bearing type, size, tolerances, cage type, load, lubricating conditions, and cooling conditions.
The allowable speeds listed in the bearing tables for grease and oil lubrication are for normal tolerance NTN bearings. In general, deep groove ball bearings, angular contact ball bearings, and cylindrical roller bearings are most suitable for high speed applications.
Bearing tolerances
The dimensional accuracy and operating tolerances of bearings are regulated by ISO and JIS standards. For equipment requiring high tolerance shaft runout or high speed operation, bearings with Class 5 tolerance or higher are recommended. Deep groove ball bearings, angular contact ball bearings, and cylindrical roller bearings are recommended for high rotational tolerances.
Rigidity
Elastic deformation occurs along the contact surfaces of a bearing’s rolling elements and raceway surfaces under loading. With certain types of equipment it is necessary to reduce this deformation as much as possible. Roller bearings exhibit less elastic deformation than ball bearings. Furthermore, in some cases, bearings are given a load in advance (preloaded) to increase their rigidity. This procedure is commonly applied to deep groove ball bearings, angular contact ball bearings, and tapered roller bearings.
Misalignment of inner and outer rings
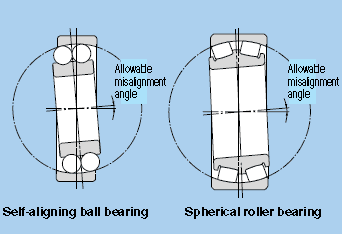
Shaft flexure, variations in shaft or housing accuracy, and fitting errors. result in a certain degree of misalignment between the bearing’s inner and outer rings. In cases where the degree of misalignment is relatively large, self-aligning ball bearings, spherical roller bearings, or bearing units with self-aligning properties are the most appropriate choices.
Noise and torque levels
NTN rolling bearings are manufactured and processed according to high precision standards, and therefore generally produce only slight amounts of noise and torque. For applications requiring particularly low-noise or low-torque operation, deep groove ball bearings and cylindrical roller bearings are most appropriate.
Installation and disassembly
Some applications require frequent disassembly and reassembly to enable periodic inspections and repairs. For such applications, bearings with separable inner/outer rings, such as cylindrical roller bearings, needle roller bearings, and tapered roller bearings are most appropriate. Incorporation of adapter sleeves simplifies the installation and disassembly of selfaligning ball bearings and spherical roller bearings with tapered bores.

